A Quick Overview: Types of IP
Type of Intellectual Property (IP) protection needed for an invention depends on the nature of invention. Each of 4 main types of IPR – Patents, Trade Secrets, Copyrights & Trademarks has their own use cases. Patents are best suited for inventions that revolve around a product – process of manufacturing, its layout or appearance etc. This brings into perspective the importance of strategies for patent monetization in leveraging the commercial potential of patents.
If you wish to protect a recipe or a formula, keeping it as a trade secret shall be the best choice. Copyrights protection is well suited for artistic works like music. Trademarks are the best way to protect the visuals that represent a brand.
Each type of IPR protection costs different, this post shares great insights on costs related to each type of IP protection.
To Patent or Not To Patent: Inventor’s Choice
In August 2010, two MIT alums filed a patent for an application that helps multiple clients share and access files over a network. There are high chances that you’ve used this file-sharing app. You must have used “Dropbox”, Haven’t you? Today, it has more than 14 million users and is a billion-dollar enterprise.
Not every founder, inventor or developer is as generous as Linus Torvalds, who gave his masterpiece (LINUX) to the world for free?
If the founders (Drew Houston & Arash Ferdowsi) of Dropbox Inc. hadn’t protected their asset by patent, Dropbox might have even had 10 times its user base today, but they wouldn’t benefit from it. This is why individuals and organizations should safeguard their intellectual property.
Most organizations are wary about the costs involved in protecting their intellectual assets. There is an assumption that it costs a bomb to get it secured. In addressing these concerns, developing a global patent portfolio strategy becomes essential to manage costs effectively. While there is no easy answer on how much it costs to safeguard your intellectual property, the safest answer is – “it depends on a lot of factors”. In this article, we will help you traverse the difficult terrain of intellectual property and your IP-related costs.
What Is Intellectual Property?
The intangible creations of the human mind are called intellectual property. It refers to inventions such as literary work, artistic work, designs, symbols, names, product recipes, images, and so on. To ensure that others do not steal your intellectual property, you need to secure them.
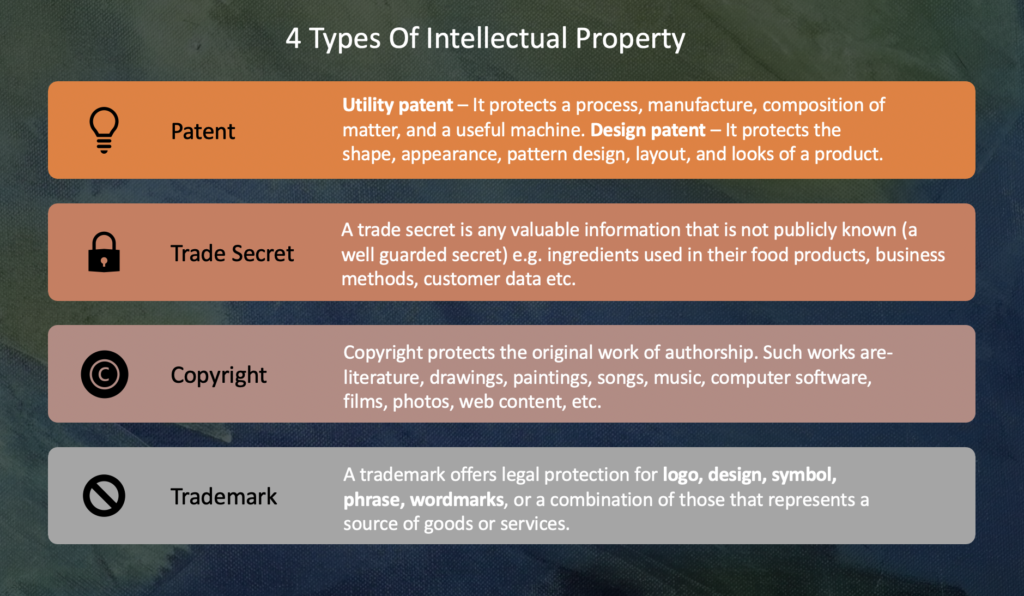
There are four different types of intellectual property (IP) rights.
- Trademark
- Patent
- Copyright
- Trade Secret
Trademark:
An American conglomerate filed a lawsuit against a Chinese company for using a brand name that was eerily similar to theirs. Even though the courts found that there were dissimilarities in products, since the latter was able to acquire clients and capture significant market share using the brand name, they had to pay up the American company.
What Is A Trademark?
It protects brands. Under the law, a trademark is anything by which customers recognize a brand or the source of a product. A trademark offers legal protection for logo, design, symbol, phrase, wordmarks, or a combination of those that represents a source of goods or services.
Example:
Credits: Legalwiz
Costs For Securing Trademark Rights in USA:
According to USPTO, the initial application fee for electronic filing for a trademark is $225 per class of goods/services. There are 45 classes of goods and services.
#1. Your attorney will file a trademark application for you and the charges for it will be anywhere between $300 and $1000.
#2. Once the application is filed, it will be examined by a Trademark Examiner.
#3. If the examiner issues an Office Action refusing the application, then the attorney’s fees to respond to that would be between $200 and $2000.
#4. The application needs to be filed based on having used the mark already for sales or with an intent to do so in the future. A Statement of Use is filed if nothing has been sold using the mark. The government’s fee to file it is $100 for each class of goods. Attorney fees to prepare it is between $250 and $700.
#5. After your application has matured to registration, you must fill the required maintenance documents. Between the 5th and 6th year of registration, Section 8 declaration has to be filed.
i.) A Section 8 declaration is a signed statement saying that the trademark is in use in commerce and if not, then it should come with an excuse explaining the reasons.
ii.) Between the 9th and 10th year after registration, a combined declaration of use/non-use and application for renewal under Sections 8 and 9 should be filed together. The fee for combined filing is $425 per class of goods or services.
For a detailed account of the trademark fee, you can use this link here.
How Long Does The Trademark Protection Last?
While the terms of trademark registration can differ, the duration is usually ten years. Also, the USPTO requires that between the fifth and sixth year after the date of registration, the trademark owner should file an affidavit stating that the mark is still being used commercially. If the affidavit is not filed, the registration is cancelled. The USPTO will not send any reminders requesting you to send the affidavit.
Note: The trademark can be renewed indefinitely by paying additional fees.
Patent:
One of the most famous patented inventions is the electric lightbulb. Another significant one is the telephone (Transmitter and Receiver for Electric-Telegraphs) which was patented by Alexander Graham Bell in 1876. Each of these made the patent owners significantly wealthy.
Credits: Google Patent
What Is A Patent?
Patents protect the innovative ideas of processes. There are two types of patents:
- Utility patent – It protects a process, manufacture, composition of matter, and a useful machine. Example: Fully convertible high heel-to-flat shoe
- Design patent – It protects the shape, appearance, pattern design, layout, and looks of a product. Example: Car or similar article by Warner Bros. (BatMobile)
Costs For Filing A Patent in USA:
For filing a patent, the costs vary not only based on the country, but also on the complexity of the invention. It could be $1000 if you plan to do most of the filing work or can be upwards of $40,000+ if your invention is complex.
The basic cost to file a patent application at the USPTO is $300. If you are an individual, and it is $75 and $150, if you are a small entity.
For professional attorney patent searches, it would cost anywhere between $800 and $3000. Find the best tips to hire a patent attorney here.
Expect to pay anywhere between $3000 and $5000 on average plus the USPTO fees to an attorney to prepare a new patent application.
The costs for the patent depends on the type of patent you apply for.
Provisional Patent: $1500 – $3500
Utility Patent: $5000 – $15000
Design Patent: $2000 – $3500
Plant Patent: $4500 – $8000
International Patent- $100000+
Here is the USPTO link where you can find more information about the fees for filing a patent.
Also, the 2025 USPTO Fee Schedule Just Dropped. Inventors and enterprises must not overlook this update.
If you want a cheaper route, then you can do all of this by yourself, but you need to be meticulous in terms of recording everything about your invention. You might have to spend hours filing everything correctly.
Choosing Inventions For Patenting
While every innovation of your invention deserves a patent, it might not be feasible to patent everything as the prices are a bit steep. To effectively manage this decision-making process, discovering the benefits of idea management software can be highly beneficial. Not everyone has huge budgets so corporations may have to pick and choose on what to patent (according to the strategy that they might have). You need to evaluate your ideas before you decide. The company should take the call on which part of your invention to pursue for patenting.
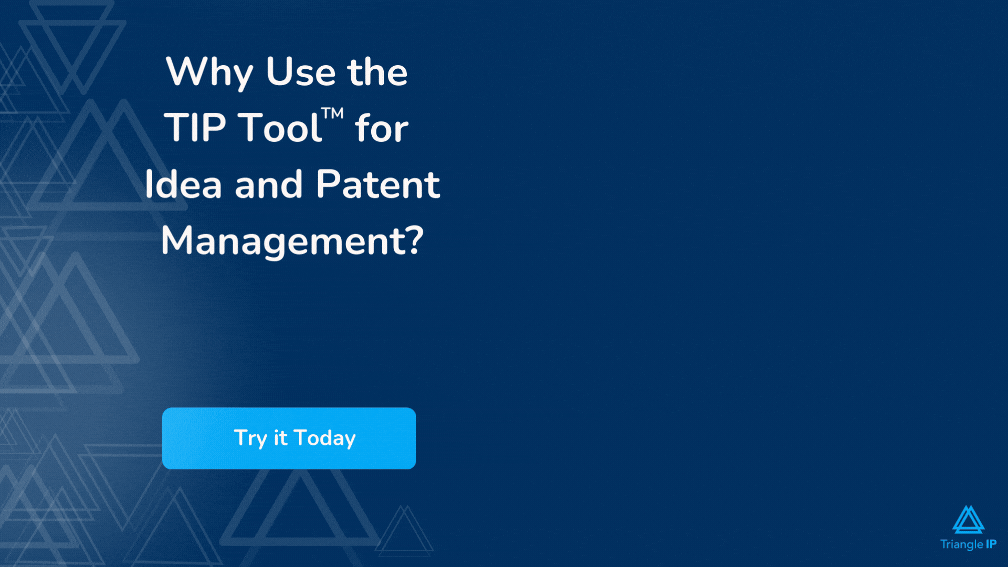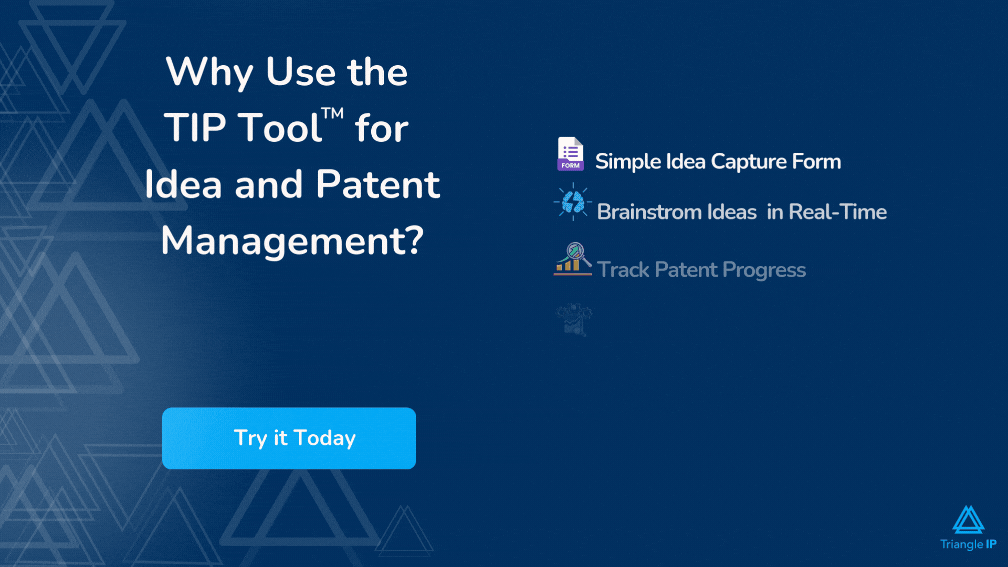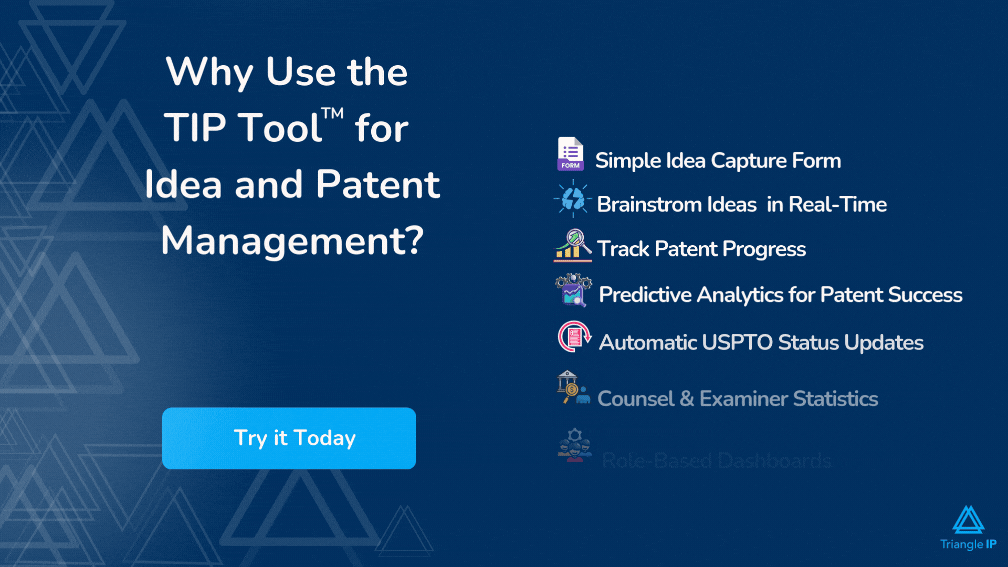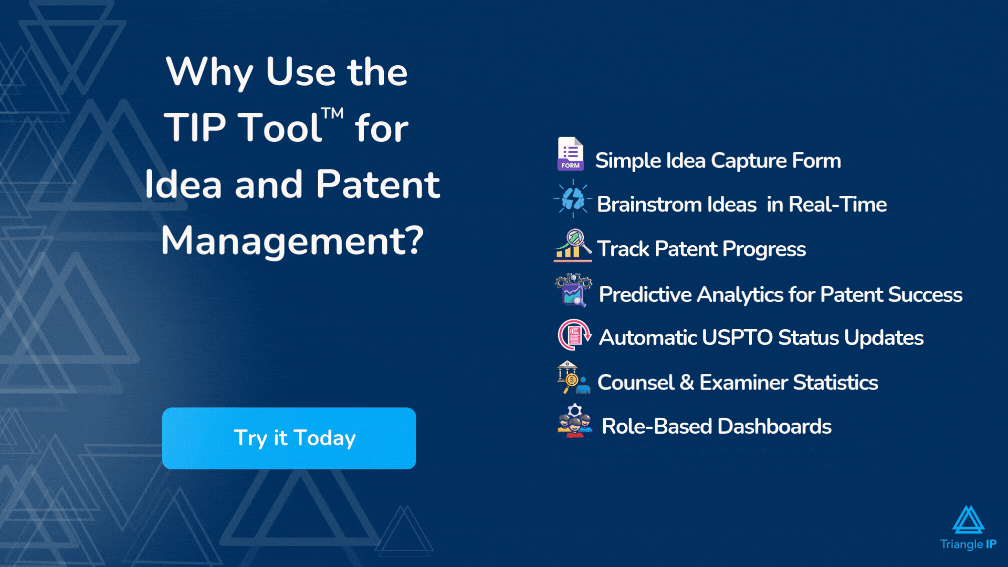
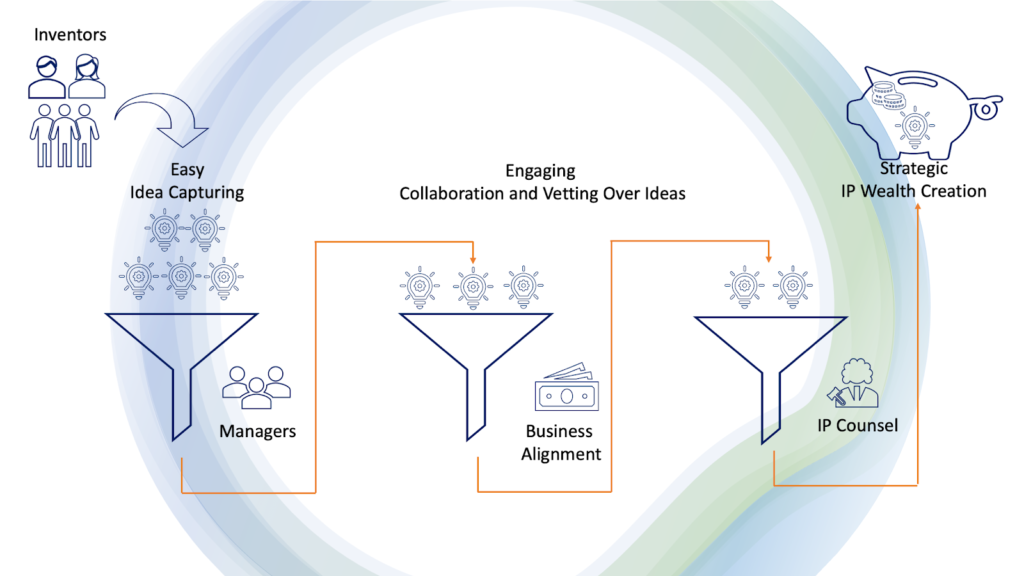
The most important part in this process is to keep a track of all ideas so that nothing is missed. You can use a simple spreadsheet but that tends to get corrupted with time along with having security issues. TriangleIP provides a free tool which helps you in maintaining and tracking your ideas. It provides you with 4 different workflow stages till the filing process – through which you can navigate and track your ideas.
Maintenance Costs:
Patent maintenance fee is paid to the USPTO to keep up a granted patent and is sometimes applicable for pending patent applications. Note: Design and Plant patents do not require maintenance fees. Maintenance fees are to be paid at the fourth, eighth and twelfth year anniversary from the time the patent is granted. To calculate the maintenance fees for your patents, you can use this link from the USPTO website.
How Long Does Patent Protection Last?
A utility patent is granted for 20 years from the date the patent application is filed. A design patent is protected for 14 years from the date the patent is granted. To enforce the protection of the patent, there are fees involved.
Copyright
Vanilla Ice’s song Ice Ice Baby used parts of music from the song Under Pressure by David Bowie and Queen.
When they faced a lawsuit, Vanilla Ice confessed to sampling the work, and the case was settled out of court for an undeclared sum of money and crediting Bowie/Queen for the track.
What is Copyright?
It protects the original work of authorship. It helps the copyright owner to control reproduction, performance, adaptations, and distribution of the work. Examples of such works are- literature, drawings, paintings, songs, music, computer software, films, photos, web content, etc.
Copyright is generally attached to the work when the original work is available in a fixed medium. It means that the work has been written down on a piece of paper, saved in a storage device, or in some tangible format.
Costs for copyright protection in USA:
Filing a copyright application involves a lot of forms and each of them has different fees. Here is a breakdown of the costs involved to copyright your work.
#1. The copyright registration fees for one work by one author costs about $45 if you are filing online. The fee is $125 for paper filing.
#2. For all the other filings, it will put you back by $65.
#3. There are special fees for registering an application claim in a group or obtaining additional certificates of registration.
#4. The USPTO does special services that have a different fee format too.
How Long Does A Copyright Last?
The terms of a copyright for a work depends on a variety of factors, including whether it has been published and if yes, then the date of publication.
#1. Copyright protection lasts for the author’s entire life plus an additional 70 years, for works created after January 1, 1978.
#2. For anonymous works, or a work made for hire or a pseudonymous work, the copyright is for a period of 95 years from the year of its first publication or 120 years, whichever expires first.
#3. For works published after 1923, but before 1978 are protected for 95 years from the date of its publication.
#4. If the work was created but not published before 1978, then the copyright lasts for the life of the author plus 70 years.
Renewal:
For works that are created after January 1, 1978, the copyright is not subject to renewal registration.
Trade Secret:
In 1953, inventors at Rocket Chemical company came up with a formula at the 40th attempt and called it WD-40 – “Water Displacement, 40th Formula”. The company never patented it because trade secret seemed like a better protection and wisely so. And the company managed to keep it a secret for 50+ years. By the fiscal year 2017, gross revenue for the company, including sales of the familiar WD-40 Multi-Use as well as other products, totalled $381 million in annual revenue. It was only in 2009, that “Wired” with advanced processes like gas chromatography and mass spectroscopy managed to find out what’s inside WD-40.
What is a Trade Secret?
A trade secret is any valuable information that is not publicly known and of which the owner has taken reasonable steps to maintain secrecy. It could be ingredients used in their dishes, business methods, customer data, ideas related to your business, marketing strategy, experimental technology, etc.
Costs To Guard Trade Secrets in USA:
Since you don’t have to register with a government body for qualifying your product/business as a trade secret, there are no costs associated with it. Guarding the secret requires security measures, and these might accrue some costs.
As trade secrets costs feel nominal compared to patenting expenses, you might get tempted to opt for trade secrets. This may or may not be a good idea. Thomas Franklin, the founder of Triangle IP has shared great insights in the following video to choose between patents and trade secrets.
How Long Does Trade Secret Protection Last?
Indefinite protection to the trade secret as long as the secret is commercially viable. It will continue as long as the secret is not available to the public. Also, unlike patents or copyrights, trade secrets are protected without registration.
How To Protect Your Intellectual Property?
We have discussed the major 4 types of intellectual property and how they can safeguard your business from infringers. It is the onus of the business to protect its assets. Losing one of your assets can result in significant damages to your business. Getting the right advice from professionals will make it easy for you to protect the interests of your business.
For starters, you could write down a list of ideas, discuss them with your lawyer and decide which are the ones that are worth going after. Triangle IP helps companies with a free tool using which ideas can be managed till the filing process.
Read this to know the 9 Best IP Portfolio Management Software For Businesses In 2026
Conclusion:
In summary, below is the list of the 4 forms of intellectual property related costs discussed in this article:
| IP Form | Protects | Life (in yrs) | Prosecution & filing costs | Maintenance Cost |
| Trademark | Infringement/Damage of reputation by another company | 10 (can be renewed indefinitely) | $225-$400 per class of goods/services depending on the type of application | $425 per class of goods/services |
| Patent | It protects the commercial use of the invention without the consent of the patent owner | 20 | $75-$300 based on the size of your company | $1,600 for large entity | $800 for small businesses | $400 for micro businesses |
| Copyright | It protects the original work of an author | 70-120 yrs | Starts at $45 for e-filing | No maintenance fees |
| Trade Secret | It protects information that is crucial to a business, using which the entity has a strong competitive advantage | Lasts as long as the trade secret is viable commercially | There is no need to register with a government body to guard your trade secret | No maintenance fees |
A report from the Commission on the Theft of American Intellectual Property pegs the loss of $600 billion annually from Chinese IP theft alone. If you fail to protect your intellectual property because of the costs involved, you might end up losing a major chunk of revenue as competitors might copy it. You will lose your competitive advantage too when others claim to provide the same features that you do.
It is normal to feel overwhelmed with the rigmarole of the lengthy procedures involved in filing applications for each intellectual property, which is exactly why you should delegate it to the experts, depending on the situation.
If you wish to simplify the process, check out the 8 Best Intellectual Property Management Software in 2026
Note: The preceding is general business advice and not to be construed as legal advice. IP laws vary by country and retaining licensed legal counsel is advised to confirm this information. Any expressed or implied opinions are of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of Triangle IP or any other entity who might be associated with the presenter. We hope this content is helpful to you, but should not be relied upon without confirming the advice and accuracy with local legal counsel. Any comments or inquiries are not confidential so please discuss your issues directly with counsel